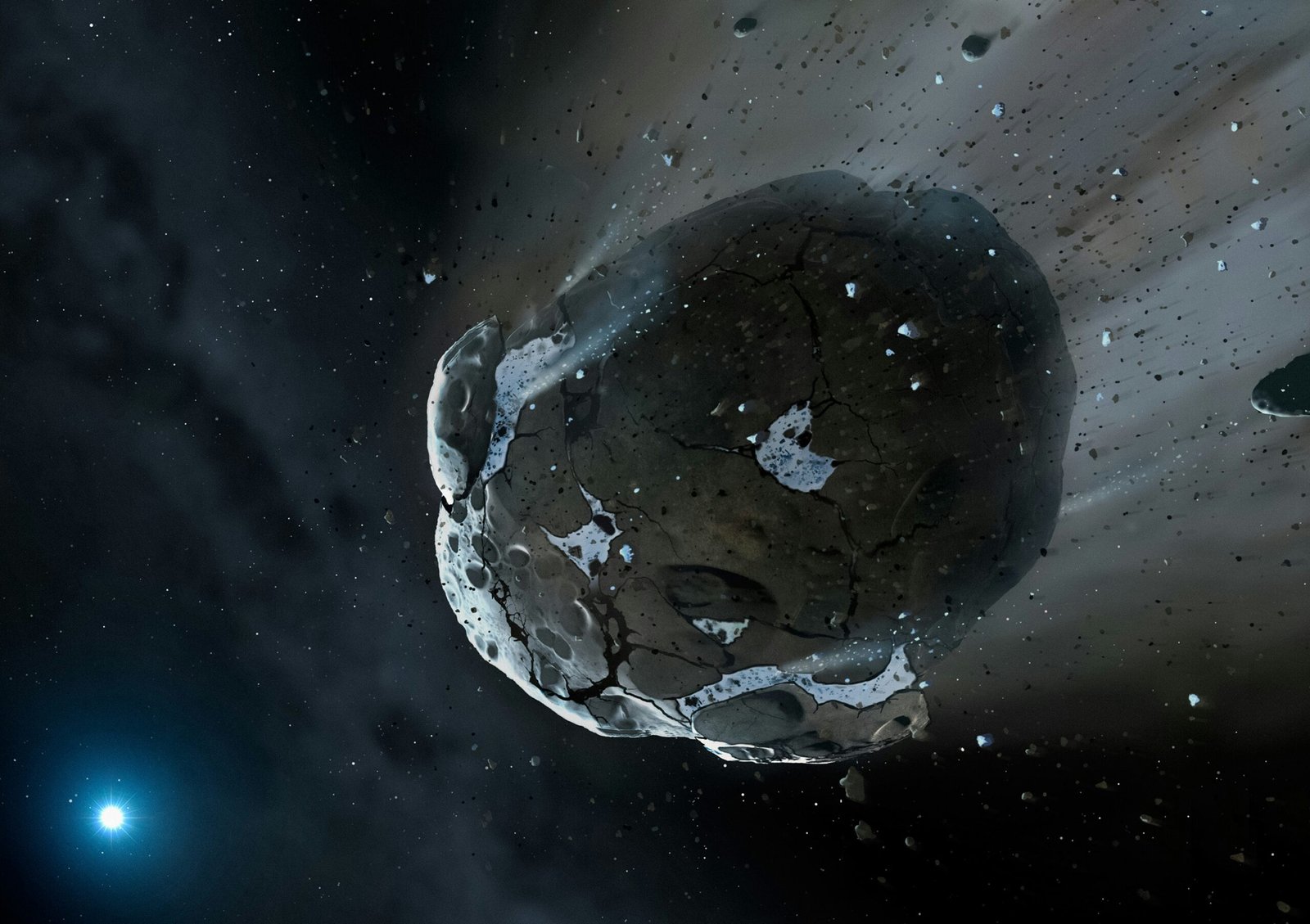
A groundbreaking astronomical discovery has captured the world’s attention. On July 1, 2025, astronomers confirmed the detection of Interstellar Comet 3I/ATLAS, only the third interstellar object ever observed. This remarkable celestial body is not just another space rock; it is the largest alien visitor yet detected, potentially spanning up to 24 kilometers. Its presence offers an unprecedented opportunity to study extraterrestrial material firsthand. As this colossal wanderer makes its closest approach to the Sun in October 2025, global telescopes are locked on. The intense public fascination is evident, with searches for this cosmic wanderer spiking daily. This discovery promises to rewrite our understanding of planetary systems beyond our own.
The Discovery of Interstellar Comet 3I/ATLAS
The Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) telescope network, funded by NASA, made the pivotal detection of Interstellar Comet 3I/ATLAS. First spotted in pre-discovery images from mid-June, its interstellar nature was confirmed by early July. Its trajectory through our solar system is hyperbolic, meaning it is not gravitationally bound to our Sun. Instead, it is merely passing through on a journey from another star system. This makes Interstellar Comet 3I/ATLAS the third confirmed interstellar object, following the enigmatic 1I/’Oumuamua in 2017 and the more conventional 2I/Borisov in 2019.
What sets this new discovery apart is its astonishing size. While ‘Oumuamua was merely hundreds of meters long and Borisov about a kilometer, 3I/ATLAS is estimated to be between 10 and 24 kilometers in diameter. This makes it a true behemoth from deep space, offering scientists a much larger sample of cosmic material to observe. Its early detection provides months of observation time, a luxury not afforded for its predecessors. This extended window allows for detailed analysis of its properties and behavior.
Unlocking Secrets: Composition of Interstellar Comet 3I/ATLAS
Early spectral analysis of Interstellar Comet 3I/ATLAS is already yielding fascinating clues about its composition. Observations confirm that it is indeed an active comet, displaying a “coma”—the characteristic fuzzy halo of gas and dust that forms as ice vaporizes near a star. This suggests its nucleus is rich in volatile ices. More recent studies, as of mid-July 2025, hint at an even more profound revelation: this object could be the oldest comet ever observed.
Researchers hypothesize that this ancient alien visitor originated from the Milky Way’s “thick disk.” This region is populated by stars billions of years older than our Sun. Comets forming in such ancient stellar nurseries are predicted to be abundant in water ice and complex organic molecules. Its initial reddish appearance further supports a primordial, unaltered composition. As Interstellar Comet 3I/ATLAS continues its approach towards the Sun, astronomers anticipate it will develop a spectacular tail, offering further opportunities to study its unique chemical makeup and unlock secrets about star formation in other galaxies.
The Scientific Goldmine and Public Fascination
The arrival of Interstellar Comet 3I/ATLAS is a scientific goldmine. For the first time, astronomers have an extended window to study an object from outside our solar system in such detail. Its unique “side-on” trajectory, differing from ‘Oumuamua and Borisov, suggests an origin from a distinct region of the galaxy. This provides invaluable data on the diversity of planetary formation processes beyond our cosmic neighborhood. This rare event allows scientists to test theories about comet composition and formation in alien star systems.
Beyond scientific circles, the public fascination is palpable. Social media platforms are abuzz with discussions, and the hashtag #AlienComet trends, fueled by the sheer wonder of an object traveling across interstellar space. While direct speculation about artificial origins (as briefly seen with ‘Oumuamua) remains a topic for discussion rather than scientific consensus for 3I/ATLAS, the term “alien visitor” perfectly captures the essence of its profound otherworldliness. This rare celestial encounter inspires awe and curiosity about what else might be drifting in the vast expanse between stars.
Tracking and Future Implications of Interstellar Comet 3I/ATLAS
Astronomers worldwide are currently using powerful telescopes to gather as much data as possible on Interstellar Comet 3I/ATLAS. It will make its closest pass by the Sun around October 29-30, 2025, just within Mars’s orbit. Despite its immense size, 3I/ATLAS poses no threat to Earth, remaining hundreds of millions of kilometers away. While not visible to the naked eye, amateur astronomers with decent telescopes may have a chance to observe it in late 2025 and early 2026 as it brightens.
The discovery of Interstellar Comet 3I/ATLAS is a testament to advancing astronomical survey capabilities. The upcoming Vera C. Rubin Observatory, expected to begin operations later this year, promises to detect many more such objects. Each interstellar visitor, whether a massive comet like 3I/ATLAS or a smaller asteroid, carries invaluable cosmic dust and ice. They serve as direct probes from distant star systems, offering us a glimpse into the chemical building blocks and conditions of exoplanetary environments. These discoveries deepen our understanding of our place in the universe and the dynamic processes that shape galaxies.
Conclusion: The detection of Interstellar Comet 3I/ATLAS marks an extraordinary moment in astronomy. As the largest and potentially oldest alien visitor ever observed, it presents an unparalleled opportunity to explore the composition of matter from distant star systems. This celestial wanderer, safely passing through our cosmic neighborhood, continues to captivate both scientists and the public. Its study will undoubtedly provide profound insights into galactic chemistry and the formation of planets beyond our Sun, pushing the boundaries of what we know about the universe.
For more news and updates, please visit PFM Today.